Why Instrument Landing System at Andaman Airport
In the realm of aviation, ensuring safe landings is paramount. Whether it’s a clear day or stormy weather, pilots rely on various tools and techniques to guide their aircraft to the ground securely. One critical aspect of this is the Instrument Landing System (ILS), which aids pilots in landing safely, especially when visibility is poor due to adverse weather conditions. In this article, we’ll explore what the Instrument Landing System entails, its significance in the airline industry, and how it operates in simple terms. : Why Instrument Landing System at Andaman Airport

What is the Instrument Landing System?
The Instrument Landing System, commonly referred to as ILS, is a precision landing aid used by pilots to safely guide their aircraft to the runway, particularly when visibility is limited due to factors like fog, rain, or low clouds. It provides accurate guidance from the final approach phase to touchdown, even when pilots cannot see the runway with their own eyes. : Why Instrument Landing System at Andaman Airport
Key Components of the Instrument Landing System
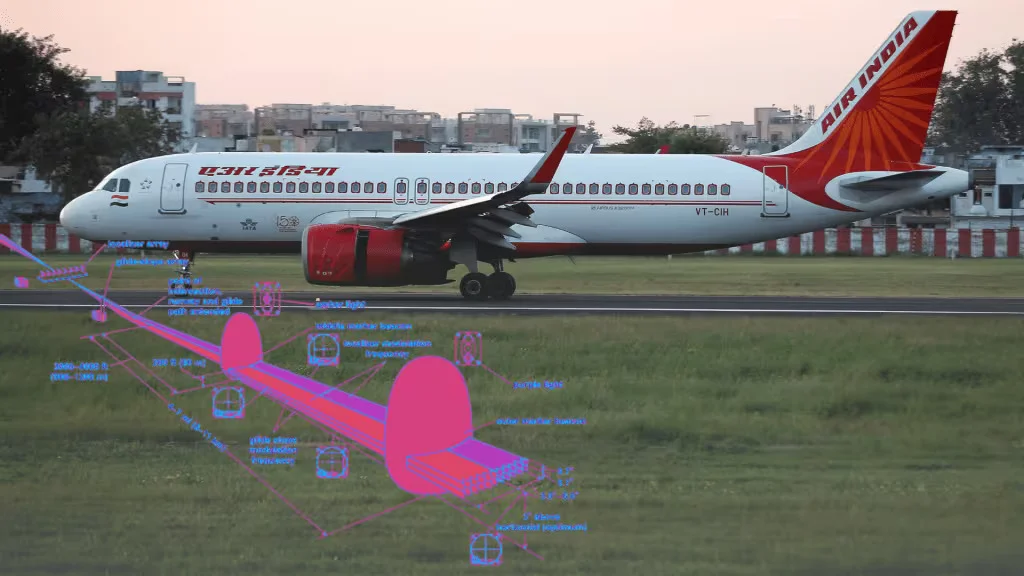
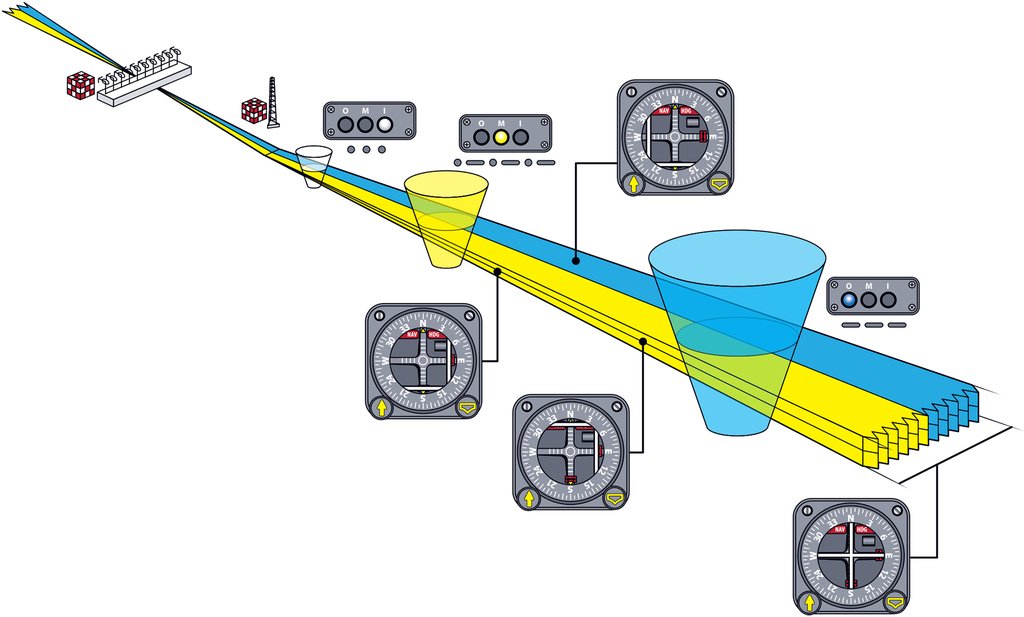
The Instrument Landing System comprises several essential components that work together to assist pilots during the landing process:
- Localizer (LOC): This component consists of a ground-based radio transmitter located at the far end of the runway. It emits signals that help pilots maintain lateral alignment with the centerline of the runway.
- Glide Slope (GS): The Glide Slope transmitter is positioned near the runway threshold. It emits signals that guide the aircraft along the correct descent path, ensuring it approaches the runway at the proper angle.
- Marker Beacons: Marker beacons are radio beacons positioned along the approach path. They provide pilots with distance information from the runway threshold, marking key points such as the outer marker, middle marker, and inner marker.
- ILS Receiver: Installed on the aircraft, the ILS receiver captures and interprets signals transmitted by the localizer and glide slope transmitters. This information is then displayed to the pilot on the aircraft’s instruments. : Why Instrument Landing System at Andaman Airport
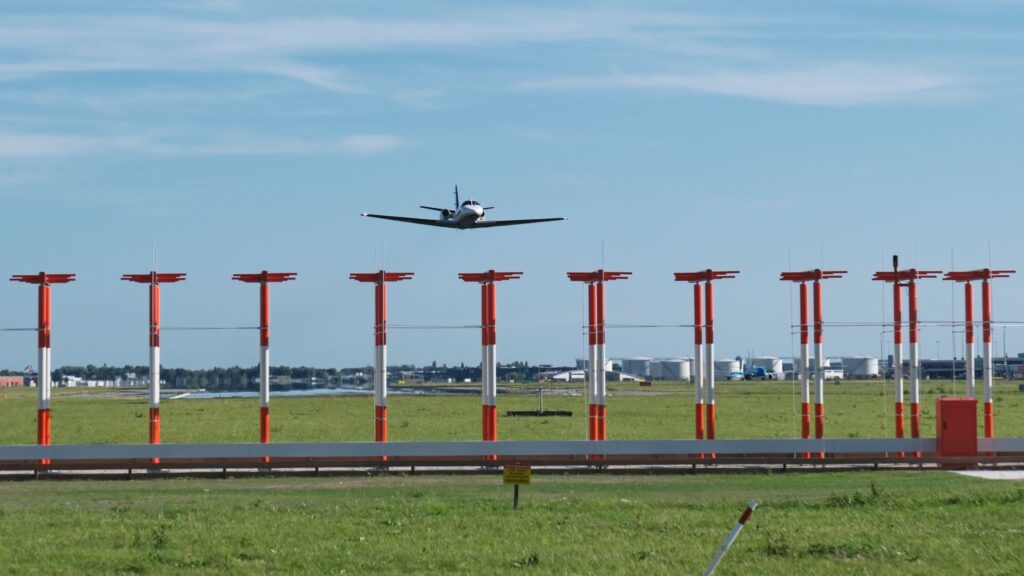
How Does the Instrument Landing System Work?
During an instrument landing approach, pilots tune the onboard navigation equipment to the frequencies corresponding to the localizer and glide slope transmitters for the intended runway. As the aircraft approaches the airport, it intercepts signals from these transmitters.
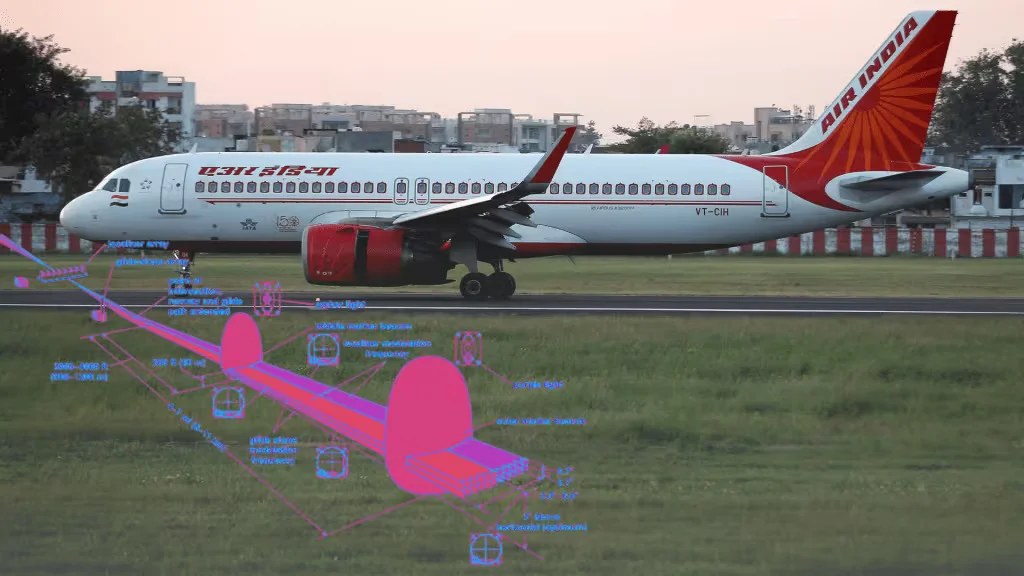

The localizer provides lateral guidance, ensuring the aircraft remains aligned with the runway’s centerline, while the glide slope guides it along the correct descent path. Pilots use the information displayed on their instruments to adjust the aircraft’s heading and descent rate to stay on course.
Significance of the Instrument Landing System in the Airline Industry
The Instrument Landing System holds significant importance in the airline industry for several reasons:
- Enhanced Safety: By providing precise guidance during landings, the ILS enhances safety, especially in adverse weather conditions with poor visibility.
- Operational Efficiency: It enables aircraft to operate in a wider range of weather conditions, reducing delays and cancellations caused by low visibility.
- Improved Accessibility: Airports equipped with ILS can accommodate flights during low-visibility conditions, improving accessibility to various destinations.
- Regulatory Compliance: Many aviation authorities mandate ILS equipment for certain operations, ensuring compliance with safety standards.
Instrument Landing System is a critical component of modern aviation, aiding pilots in safely navigating their aircraft to the runway, even in challenging weather conditions. Its precision guidance enhances safety, operational efficiency, and accessibility in the airline industry, making it an indispensable tool for pilots worldwide.
Why Instrument Landing System at Andaman Airport





